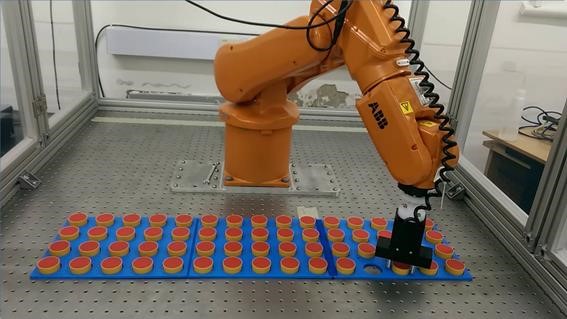
Benchmarking dexterity in flexible manufacturing (2013-2017)
In order to meet future consumer demands, such as more customisable and personal products, there is a current shift within industry towards more customisable and flexible manufacturing. This will require the development of robots with performance parameters such as adaptability and flexibility. An important enabler of these is the development of robotic dexterity, or more specifically manipulative dexterity, which is paramount in order for robot arms to perform tasks that require grasping and in-hand manipulation of objects. To address the above, this project has explored the current state of manipulative dexterity and has developed a novel approach to benchmarking the parameter
This research explored how existing methods for benchmarking human dexterity, namely the Boothroyd-Dewhurst (B-D) Design-For-Assembly method, might be be effectively adopted to form the basis of a comprehensive robotic dexterity assessment within flexible manufacturing.