Introduction to Programme and Module Design

In this page we will briefly consider the nature of curriculum development and how constructive alignment can be used in programme and module design.
Curriculum Development
According to Ornstein and Hunkins (2009, p15) the curriculum development process involves how the ‘curriculum is planned, implemented and evaluated, as well as what people, processes and procedures are involved’. There are a broad range of approaches to curriculum development, therefore it is important to consider the approach best suited to your context, prior to the design of a programme or module.
For further information on the approaches to curriculum development see our resources on Curriculum Design.
Programme & Module Design
Curriculum alignment is the process of ensuring that the intended learning outcomes, of a programme and/or module, are coherently mapped to the assessment and teaching and learning strategies adopted.
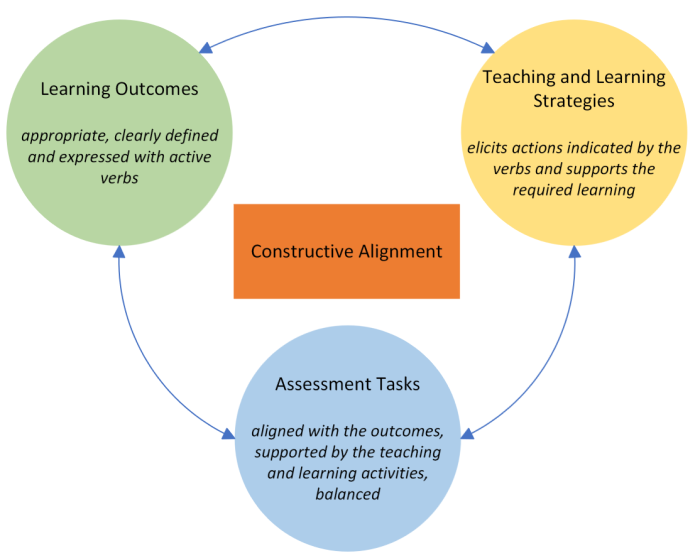
Curriculum alignment can be achieved by the development of programmes, modules and electives that follow a constructive alignment model. The three key components of curriculum alignment: (1) intended learning outcomes are appropriate and clearly defined; (2) teaching and learning strategies support the required learning, and (3) the assessment tasks are balanced and aligned with the outcomes (Biggs, 1996, 2003).
Learning outcomes influence module content, delivery mode, and assessment strategy. In curriculum design terms, constructive alignment is desirable (e.g. coherence between assessment activity, teaching and learning activities, and learning outcomes). Clearly articulating learning outcomes for a programme or module is an essential step in curriculum design with important implications for teaching, learning, and assessment.
Programme and Module Design - what needs to be considered
- Who are the targeted learners and what are their specific needs?
- How will the programme or module be delivered, online, in-person or a combination of these?
- What is the aim of the programme or module and what learning outcomes are to be achieved by the learners?
- How should the learning outcomes be assessed?
- What teaching strategies can be used to support learners in achieving the learning outcomes?
Follow the links on the left hand navigation bar for further information on designing programmes and modules.
Key Takeaways
Constructive alignment is a key element of designing successful programmes and modules which is achieved by;
- Defining clear and assessable learning outcomes
- Selecting appropriate assessments
- Using teaching strategies that support the required learning
Establishing learner needs at the outset will help inform effective design, development and implementation of programmes and modules.
Click on the links below to open the section(s).
References
Biggs, J., 1996. Enhancing teaching through constructive alignment. Higher education, 32(3), pp.347-364.
Biggs, J., 2003. Aligning teaching for constructing learning. Higher Education Academy, 1(4).
Ornstein A.C. & Hunkins, F.P. (2009). Curriculum foundations, principles and issues. (5th ed). Boston: Allyn and Bacon

