Unstable Path Routing in Urban-Scale WSN
Smart cities will exploit the wide array of data available from sensors deployed by city authorities and public utilities as well as from user-contributed sensors. Many of these sensors are resource-constrained, which makes large-scale data collection challenging. Smart mobile devices, which are abundantly present in modern urban environments can be leveraged to offload communication from the resource-constrained sensors. The paths established by these smart mobile devices are inherently unstable due to their mobility and the actions of their users, and the routing must fulfil conflicting objectives in terms of fault tolerance, energy, congestion prevention and latency.
State of the art
In all existing protocols, scanning is performed by resource-constrained sensors. The existing routing protocols that consider the presence of mobile devices in WSNs. Do not offload communication from WSN. Do not consider and conciliate the conflicting objectives. The routing protocols redirecting traffic towards reliable nodes in MANET are not suitable for WSNs due to their reliance on route discovery and route repair procedures, and poor or non-existent congestion control.
Our Approach
We purpose a mobile device discovery and routing algorithm designed to minimize WSN overhead. Smart devices trigger a channel scan when a sensor network is expected and offload the communication load away from resource-constrained sensors.
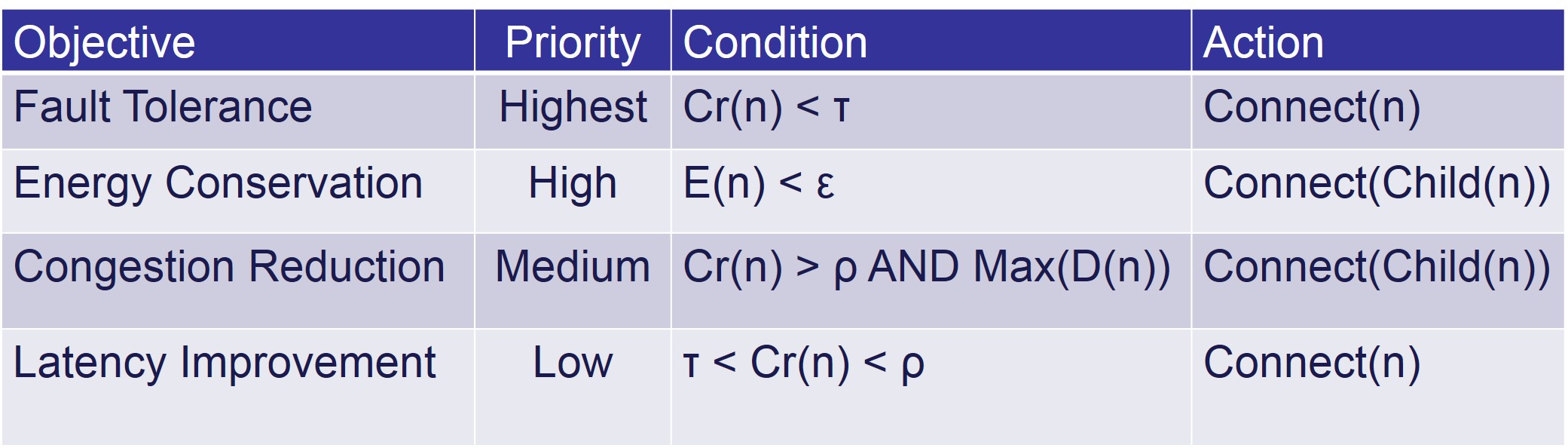
Smart devices fulfil prioritized objectives based on sensor network conditions:
Results
Comparison of conventional baseline device discovery mechanisms versus a discovery mechanism optimized for WSN.
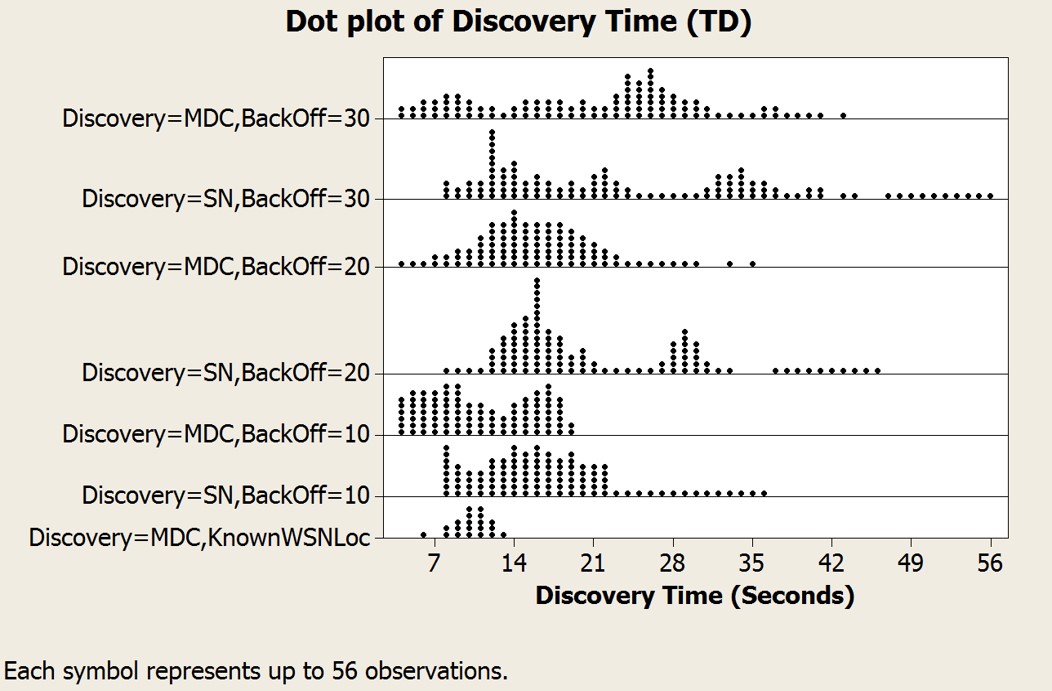
Lower discovery time interval achieved when a smart device scans the radio channel when it expects a WSN in range.
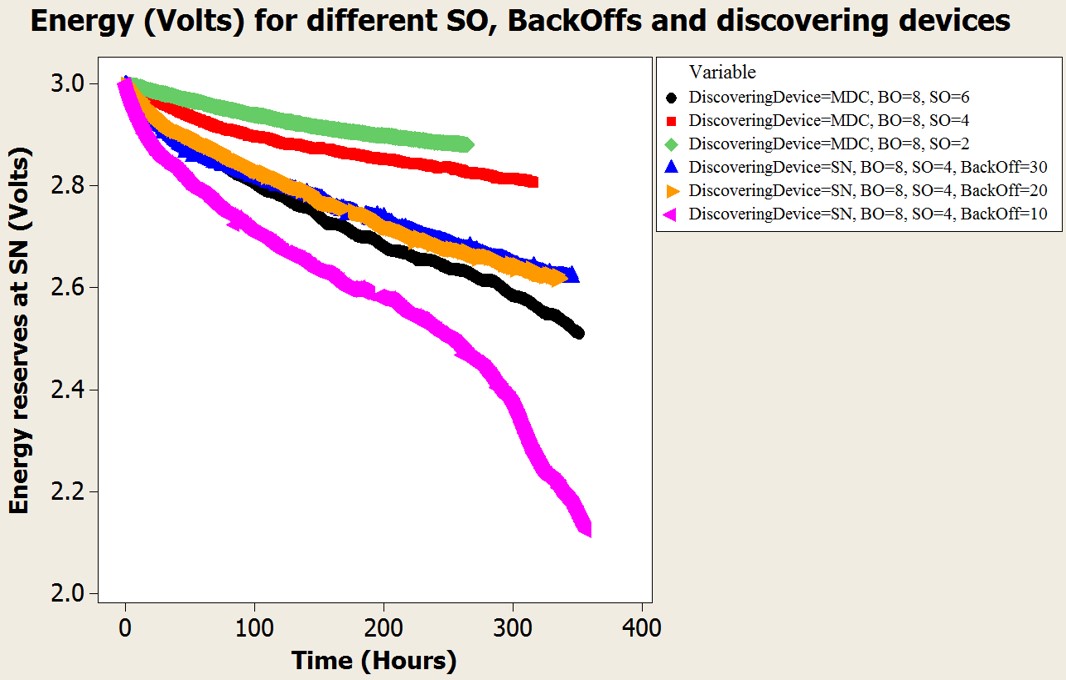
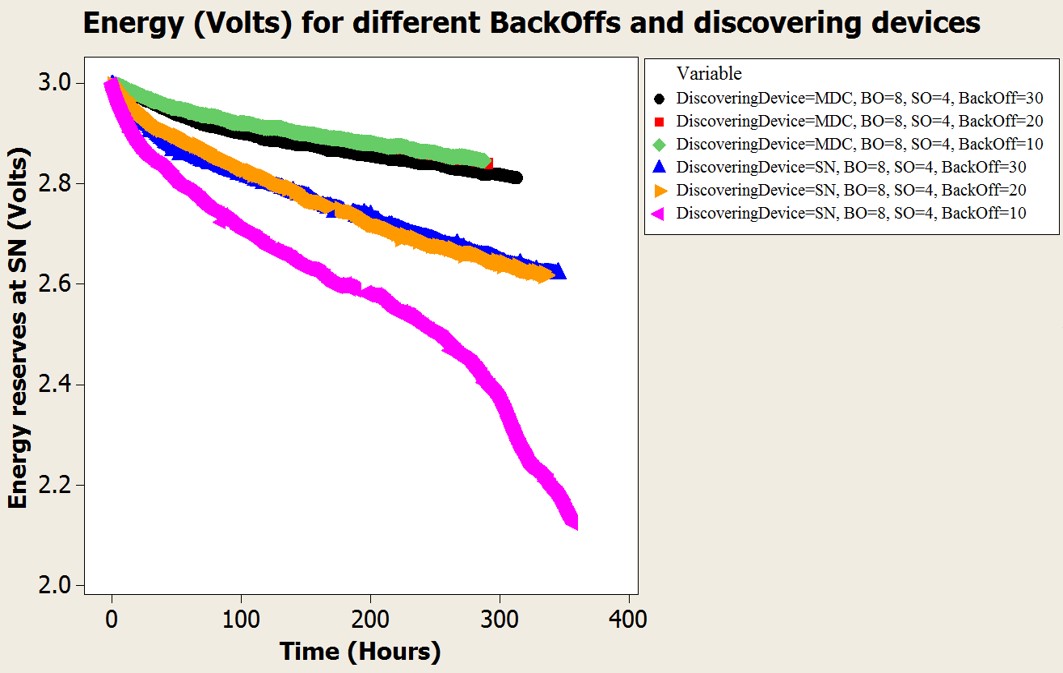
Better energy consumption at the sensors is achieved when a smart device scans the radio channel, given that the proper duty cycle is set at the sensor.
When a smart device scans periodically, the discovery duty cycle has no impact on the energy consumption at sensors.
Conclusions
We have presented the novel device discovery protocol for WSN, which reduces energy consumption at sensors and improves the discovery time interval. This routing protocol for WSN outsources communication to smart devices,reduces end-to-end latency and congestion at critical nodes. It also provides fault tolerance in network partitions.
People
Farrukh Mirza, Mélanie Bouroche, Vinny Cahill
Sponsors