Issues in agricultural and food markets
-
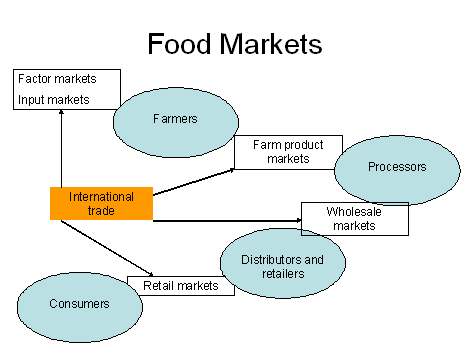
- Primary commodity markets
- competitive markets - characterised by volatility, declining terms of trade, bargaining weakness of farmers, may not guarantee food security at either the household or national level
- Factor and resource markets
- missing and imperfect markets (environment, agricultural research)
labour market (concerns over income levels), land markets (managing competing uses)
- Input and food wholesale markets
- concentrated markets - suffer from concerns over market power, role of advertising, brands
- Food retail markets
- changing consumer behaviour (diets, nutrition), asymmetry of information (food safety, food quality)
- International trade markets
- Level playing field?, fair trade, disease spread, food miles
-
Government regulation of agricultural and food markets
- Most countries adopt an active agricultural policy to address these perceived weaknesses in food and agricultural
markets. Thus there is evidence that policy addresses significant and widespread socio-economic problems. However....
- Note the high levels of border protection far exceeding anything we find in the industrial or services sectors
- Note the high transfers from consumers and taxpayers to agriculture (OECD PSE estimates)
- Note the frequency of trade disputes around issues to do with agricultural trade barriers and food safety
- Are these costs simply a fair price which society is prepared to pay to achieve valid objectives? What are
these objectives? Are they being met by existing policies? Could they be met more cheaply? This is the leitmotiv
of this course.
The policy analysis perspective
How does the economist approach these issues? The following is a useful checklist.
- What objectives is the policy trying to achieve?
- What instruments is it using?
- Is the intervention efficient?
- Is the intervention equitable?
Reading suggestions
Matthews, A., 2004, 'Agriculture, food safety and rural development', in O'Hagan, J. and Newman, C., eds The Economy of Ireland,
9th edition, Macmillan, Dublin.
(read for a general introduction to issues raised in the course from an Irish perspective. Note that this is a more recent edition that the one you studied in second year. Download chapter from 9th edition)
Matthews, A., 2003, 'Agriculture', in Johnson, P. ed., Industries in Europe: Competition, Trends and Policy Issues, Cheltenham, Edward Elgar, pp. 26-54.
Rabinowicz, E., 1999, 'Redesigning the CAP to meet the challenges of EU enlargement and the WTO: what can agricultural economic research contribute?' Eur. Review of Agric. Econ. 26, 3, 265-281.
(this Presidential Address to the European Association of Agricultural Economists introduces some of the issues which this course will address).
Supplementary reading
For a recent review of policy issues in Irish agriculture, see
Report of the Agri-Vision 2015 Committee, 2004, Department of Agriculture and Food (file size 521KB)