Universal Re-usable Energy Absorption Devices (UREAD)
Project CoordinatorDr Rocco Lupoi
Email: [javascript protected email address]
Tel: +353 1 896 1729
A unique novel technique for energy dissipation is currently under development within Trinity College Dublin. The technique is implemented into a device that absorbs impact force or energy through a reversible internal mechanism without distorting the structural integrity or geometry of the device. The device is comparatively cheap to manufacture and can be used in engineering applications such as protection against unexpected impact, in-line force limiting applications and protection buffers. The device has no spring back or direct reaction force, has 100% re-usability, and requires zero maintenance. Its versatile design enables several units to be linked together to form protection joints which can be used in trusses, buildings, structures, and could provide protection against earth quakes and vibrations.
These units are fool-proof and provide energy dissipation technology that withstands forces as small as few Newtons like those experienced in machine tool end-stops, to over mega Newtons such as those delivered through aircraft landing gear. Other immediate applications include safety rails, crash barriers and energy decelerators.
The end user market for this device covers the automotive industry, machine tools, locomotives, aerospace, marine, defence, building, sports and numerous engineering safety applications.
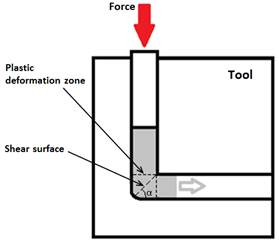
Figure 1: Shearing process of materials in 90° intersecting channels.
Advantage of this new device:
- Simple to use
- Easy to manufacture
- Cheap to produce
- Maintenance free
- Negligible fatigue effects
- Re-usable
- No rebound after impact
- Single action to activate energy dissipation
- Large range of force applications
- Wide range of applications
- Adjustable levels of energy absorption rates
- Can be integrated into existing structures

